Building Large IPv6 Service Provider Networks
Overall rating: 4.67 Instructor: 4.88 Materials: 4.80 more …
You're facing numerous design choices when building an IPv6-enabled Service Provider network: SLAAC or DHCPv6 in multi-access subnets, local or centralized addressing pools, RADIUS integration, dual-stack or MPLS-based (6PE) deployment, and IPv6 VPN (6VPE) considerations. This 5-hour advanced technical webinar addresses all these design challenges and related router configurations, and describes comparative benefits and drawbacks of every decision you could make.
We’ll also discuss Cisco IOS configurations for every single option described in the webinar, from core routers (P-routers) to provider edge (PE-) routers and customer (CPE) devices. You'll also get complete router configurations for over a dozen deployment scenarios.
To give you a blueprint for an end-to-end IPv6 deployment in a Service Provider network, the webinar describes:
- Common access-layer methods (shared LAN like WiFi or Cable networks, IPv6-over-Ethernet and IPv6-over-PPP);
- Customer attachment configurations (dial-up hosts, CPE devices with DHCP-assigned IPv6 prefixes, static routing and multi-homed enterprise customers running BGP);
- Dual-stack and MPLS-based core network.
Contents
Design Principles
This section describes common large-scale design principles and how they apply to IPv6 deployment:
- Access network is isolated from the core;
- IGP is used to establish connectivity within the core;
- BGP is used to propagate access network routes between PE-routers.
Access Network Configuration
This section describes the design choices you have when connecting business or residential customers to IPv6 services. It covers three major access technologies:
- Shared LAN subnets (example: WiFi hotspots);
- Carrier Ethernet deployments with IPv6-aware CPE devices;
- PPPoX deployments, with end-hosts or CPE devices establishing PPPoX sessions with the PE-routers.
Routing mechanisms described in this section include:
- Low-end CPE device using IPv6 prefix delegation with DHCPv6 (IA_PD option of DHCPv6);
- Static routing for single-homed business customers;
- Multihomed business customers having provider-independent (PI) IPv6 address space and running BGP with the Service Provider network.
The section also describes the intricate details you need to understand to deploy DHCPv6 prefix delegation on edge routers, including local IPv6 address pools, DHCPv6 relay and DHCPv6-RADIUS integration.
Core Network Design and Configuration
The core network part of the webinar describes dual-stack deployments, IPv6-over-MPLS (6PE) and MPLS-based layer-3 IPv6 VPNs (6VPE)
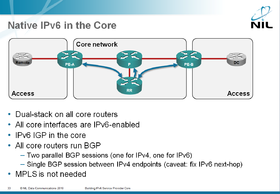
Native IPv6 Core
The Native IPv6 core design uses dual-stack approach: all core routers run IPv4 and IPv6. This section describes the consequences of this approach, including the need for AS-wide multiprotocol BGP. It covers numerous technical details, including IPv4/IPv6 BGP sessions, IPv6 BGP next-hop management and the choice of IGP (OSPFv2/v3 or multiprotocol IS-IS).
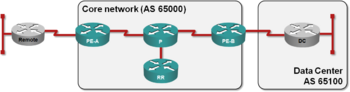
IPv6 MPLS Transport
An MPLS-enabled network core can use MPLS in combination with multiprotocol BGP to transport IPv6 across LSPs with IPv4 IGP/LDP or MPLS TE. This section describes the 6PE design and implementation guidelines and contains detailed router configuration for both PE-routers and multiprotocol route reflectors.
IPv6 in a VPN
Service providers planning to offer IPv6 VPN services might consider multiprotocol MPLS/VPN deployment; Cisco IOS allows you to configure IPv4 and IPv6 address families within a single VRF. This section describes the basics of 6VPE (MPLS/VPN for IPv6), the changes made to VRF configuration in Cisco IOS and the additional address families that have to be configured within the BGP routing process.
Exclusions
The webinar does not address product-specific details (for example, limitations of IPv6 on a specific hardware platform), low-end consumer CPE devices (Cisco routers are used as CPE devices) or details of specific access methods (for example, IPv6 over PPPoE over DSL).
Router configurations
Several sets of complete router configurations for a six router lab are included with the materials you get when buying this webinar.
The lab topology emulates a typical Service Provider network (with PE routers, P routers and a BGP route reflector) with various types of residential customer (WiFi hotspot, Carrier Ethernet using dynamic prefix allocations with DHCPv6, and PPPoE hosts and CPE devices), and an enterprise BGP customer (advertising its own IPv6 prefix via BGP).
The network core router configurations scenarios include:
- Native dual-stack (IPv4+IPv6) network with OSPFv2+OSPFv3 in the Service Provider core and parallel per-protocol BGP sessions;
- Native dual-stack network with OSPFv2+OSPFv3 in the Service Provider core and multi-protocol BGP session between IPv4 endpoints;
- Native dual-stack network with IS-IS in the Service Provider core;
- IPv4+MPLS network with IPv6 transported with 6PE functionality;
- IPv4+MPLS network offering VPNv6 services.
The access network router configuration scenarios include:
- Multi-access networks using SLAAC, local DHCPv6 and DHCPv6 relay;
- Carrier Ethernet with DHCPv6 prefix delegation using either local DHCPv6 pools or DHCPv6 relay;
- PPPoE (host and CPE device) using local address pools, DHCPv6 relay or RADIUS-based customer-side IPv6 addressing
Target audience
The presentation is ideal for advanced Service Provider and Enterprise engineers, from designers (who will probably focus on the benefits/drawbacks analysis of various transport options) to implementation engineers (who will enjoy the detailed configuration templates).
Prerequisite knowledge
The Building Large IPv6 Service Provider Networks discusses advanced IPv6, BGP, MPLS and MPLS VPN concepts. You are expected to have basic understanding of IPv6 addressing and routing, BGP design and configuration and MPLS principles of operations.

 Ivan Pepelnjak (CCIE#1354 Emeritus) has been designing, deploying, operating and troubleshooting IP-based enterprise and service provider networks since 1990. He’s the author of EIGRP and MPLS books published by Cisco Press, numerous articles and highly praised webinars, including Building Large IPv6 Service Provider Networks,
Ivan Pepelnjak (CCIE#1354 Emeritus) has been designing, deploying, operating and troubleshooting IP-based enterprise and service provider networks since 1990. He’s the author of EIGRP and MPLS books published by Cisco Press, numerous articles and highly praised webinars, including Building Large IPv6 Service Provider Networks,